PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
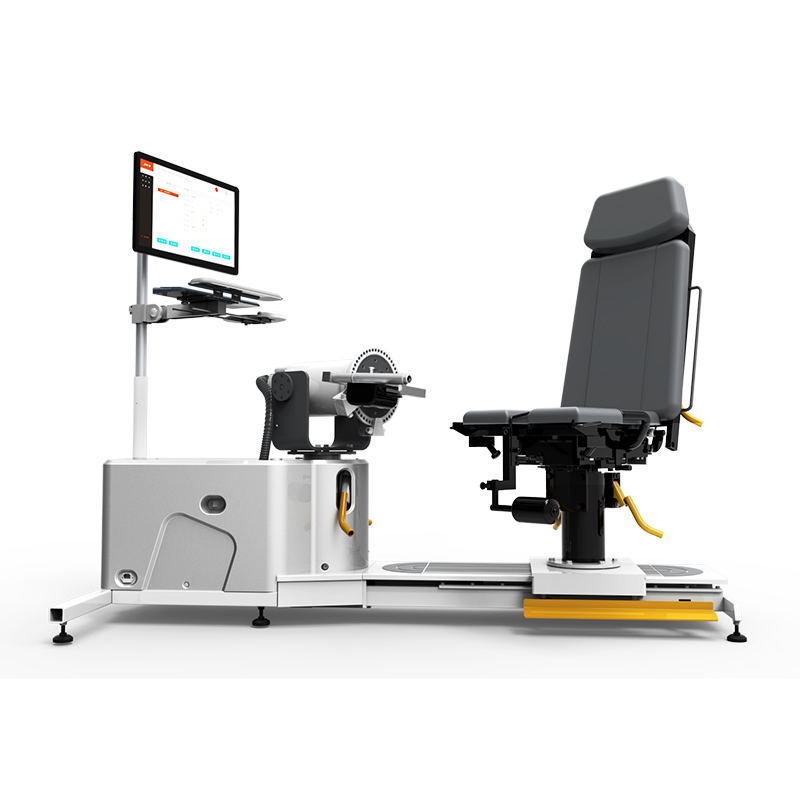
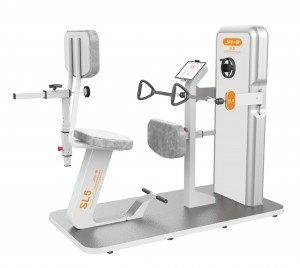
Multi-joint isokinetic training and testing system A8 is a comprehensive system for the evaluation and training of relevant programs of isokinetic, isometric, isotonic and continuous passive for six major joints of human shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee and ankle.
After testing and training, the testing or training data can be viewed, and the generated data and graphs can be printed as a report for the assessment of human functional performance or researchers’ scientific research. A variety of modes can be applied to all stages of rehabilitation to realize the rehabilitation of joints and muscles to the maximum extend.
DEFINITION OF ISOKINETIC
Isokinetic motion refers to the motion that speed is constant and resistance is variable. The motion speed is pre-set in the isokinetic instrument. Once the speed is set, no matter how much force the subject uses, the speed of the limb movement will not exceed the pre-set speed. The subject’s subjective force can only increase muscle tone and torque output, but can not produce acceleration.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ISOKINETIC
Accurate Strength Testing – Isokinetic Strength Testing
Comprehensively reflect the strength that the muscle groups exert at each joint angle.
The differences between the left and right limbs and the ratio of antagonistic/ agonistic muscle are compared and evaluated.
Efficient and Safe Strength Training — Isokinetic Strength Training
It can apply the most appropriate resistant for patients at every joint angle.
The resistance applied will not exceed patient’s limit, and it can reduce the applied resistance when patient’s strength decreases.
INDICATIONS
Motor dysfunction caused by sports injuries, orthopaedic surgery or conservative treatment, nerve injuries and other factors.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fracture risk; acute phase of disease course; severe pain; severe joint mobility limitation.
CLINICAL APPLICATION
Orthopedics, neurology, rehabilitation, sports medicine, etc.
FUNCTIONS & FEATURES
1. Evaluation and training of 22 movement modes for six major joints of shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee and ankle;
2. Four motion modes of isokinetic, isotonic, isometric and continuous passive;
3. A variety of parameters can be evaluated, such as peak torque, peak torque weight ratio, work, etc.;
4. Record, analyze and compare test results and improvement;
5. Dual protection of motion range to ensure patients test or train in the safe range of motion.
ORTHOPEDIC REHABILITATION CLINICAL PATHWAY
Continuous Passive Training: Maintain and restore range of motion, alleviate joint contracture and adhesions.
Isometric Strength Training: Relieve disuse syndrome and initially enhance muscle strength.
Isokinetic Strength Training: Quickly increase muscle strength and improve muscle fiber recruitment ability.
Isotonic Strength Training: Improve neuromuscular control ability.