Stroke is characterized by high incidence rate and high disability rate. There are approximately 2 million new stroke patients in China every year, of which 70% to 80% are unable to live independently due to disabilities.
The classic ADL training combines restorative training (motor function training) and compensatory training (such as one-handed techniques and accessible facilities) for joint application. With the development of medical technology and emerging technologies, more and more technologies have been applied to the training of ADL.
The upper limb rehabilitation robot is a machine device used to assist or replace certain upper limb functions of humans in automatically executing tasks. It can provide patients with high-strength, targeted, and repetitive rehabilitation training. In promoting functional recovery in stroke patients, rehabilitation robots have significant advantages over traditional treatments.
Below is a typical case of a hemiplegic patient using robot training:
1. Case Introduction
Patient Ruixx, male, 62 years old,admit due to “13 days of poor left limb activity”.
Medical history: On the morning of June 8th, the patient felt weakness in their left upper limb and was unable to hold objects. At noon, they developed weakness in their left lower limb and were unable to walk, accompanied by numbness in their left limb and unclear speech. They were still able to understand others’ words, disregarding object rotation, no tinnitus or ear examination, no head pain, heart vomiting, no black eye syncope, no coma or convulsions, and no urinary incontinence. Therefore, they came to our emergency department for further diagnosis and treatment, The emergency department plans to treat the Neurology of our hospital with “cerebral infarction”, and give Symptomatic treatment such as anti platelet aggregation, lipid regulation and plaque stabilization, brain protection, promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, anti free radicals, acid suppression and stomach protection to prevent Irritability ulcer, improve collateral circulation, and monitor blood pressure. After treatment, the patient’s condition remained relatively stable, with poor left limb movement. In order to further improve limb function, it is required to be admitted to a rehabilitation department for rehabilitation treatment. Since the onset of cerebral infarction, the patient has been depressed, repeatedly sighing, passive, and diagnosed as “post-stroke depression” in Neurology.
2. Rehabilitation assessment
As a new clinical treatment technology, rTMS needs to pay attention to operational norms when carried out in clinical medical institutions:
1) Motor function assessment: Brunnstrom assessment: left side 2-1-3; Fugl Meyer’s upper limb score is 4 points; Muscle tension assessment: Left limb muscle tension decreased;
2) Sensory function assessment: deep and shallow Hypoesthesia of left upper limb and hand.
3) Emotional function assessment: Hamilton Depression Scale: 20 points, Hamilton Anxiety Scale: 10 points.
4) Activities of daily living score (modified Barthel index): 28 points, ADL severe dysfunction, life needs help
5) The patient is a farmer by profession and currently cannot grip with their left hand, which hinders their normal farming activities. Leisure and entertainment activities have been significantly restricted since the onset of illness.
We have developed a rehabilitation treatment plan for Grandpa Rui’s functional problems and symptoms of depression, with a focus on improving the patient’s ADL function, reflecting Grandpa’s progress, enhancing self-awareness, and feeling that he is useful people.
3. Rehabilitation treatment
1) Inducing Upper Limb Separation Movement: Treatment of Affected Upper Limb Pushing Drum and Functional Electrical Stimulation
2) ADL guidance training: The patient’s healthy upper limb completes skill guidance training such as dressing, undressing, and eating.
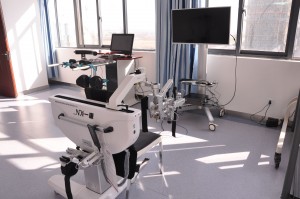
3) Upper limb robot training:

A prescription model guided by life ability. Provide daily life action prescription training to train patients’ daily living ability (ADL)
- Eating training
- Combing training
- Organize and classify training
After two weeks of treatment, the patient was able to grab bananas with his left hand to eat, drink water from a cup with his left hand, twist a towel with both hands, and his ability of daily living improved significantly. Grandpa Rui finally smiled.
4. The advantages of upper limb rehabilitation robots over traditional rehabilitation lie in the following aspects:
1) Training can set personalized movement patterns for patients and ensure that they repeat movements within the set range, providing more opportunities for targeted exercises in the upper limbs, which is beneficial for brain plasticity and functional reorganization after stroke.
2) From the perspective of Kinematics, the design of the arm bracket of the rehabilitation robot is based on the principle of human Kinematics, which can simulate the movement law of human upper limbs in real time, and the patients can observe and imitate the exercise repeatedly according to their own conditions;
3) The upper limb rehabilitation robot system can provide various forms of feedback information in real-time, making the dull and monotonous exercise rehabilitation training process easier, interesting, and easy. At the same time, patients can also enjoy success.
Because the virtual training environment of upper limb rehabilitation robot is highly similar to the real world, the motor skills learned in the virtual environment can be better applied to the real environment, prompting patients to interact with objects with multiple sensory stimuli in the virtual environment in a natural way, so as to better mobilize patients’ enthusiasm and participation in rehabilitation, and further improve the motor function of the upper limb on the hemiplegic side and the ability of Activities of daily living.
Author: Han Yingying, group leader of occupational therapy in the Rehabilitation Medical Center of Jiangning Hospital affiliated to Nanjing Medical University
Post time: Jun-16-2023