Preschool spinal scoliosis not only affects the skeletal development and respiratory function but also causes chest deformities and even impacts the psychological health of children.
1. What is spinal scoliosis?
Spinal scoliosis is a three-dimensional deformity of the spine characterized by a Cobb angle greater than 10° and vertebral rotation. Simply put, it is a sideways curvature of the spine, either to the left or right.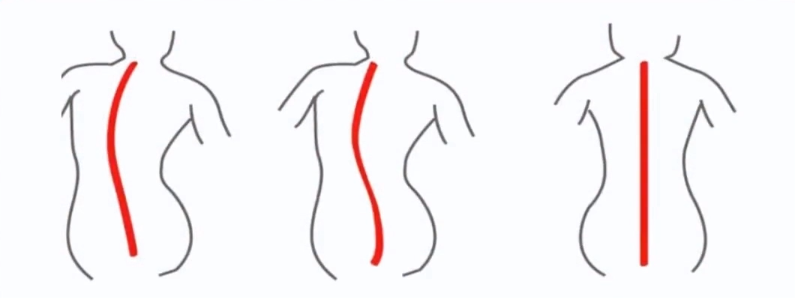
C-shaped Scoliosis S-shaped Scoliosis Normal Spinal
2. Why does spinal scoliosis occur?
- Genetic factors and certain neurologic and muscular conditions, such as muscular dystrophy.
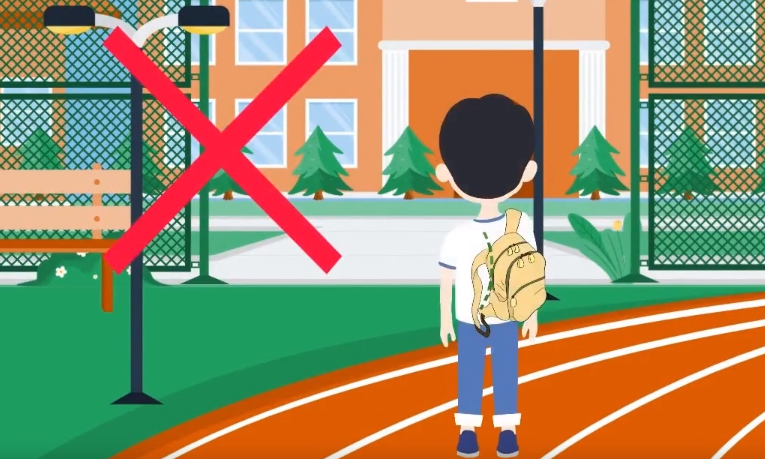
- Incorrect backpack posture.
- Insufficient physical activity and a lack of exercise.
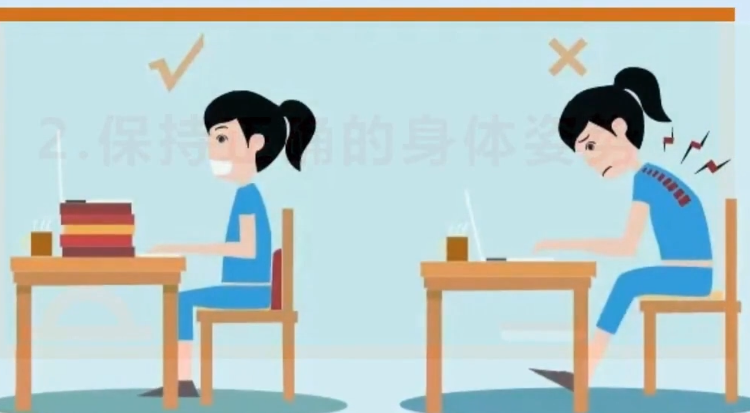
- Poor body posture, such as incorrect sitting posture.
- Excessive body weight.
3. How is spinal scoliosis diagnosed if there is suspicion?
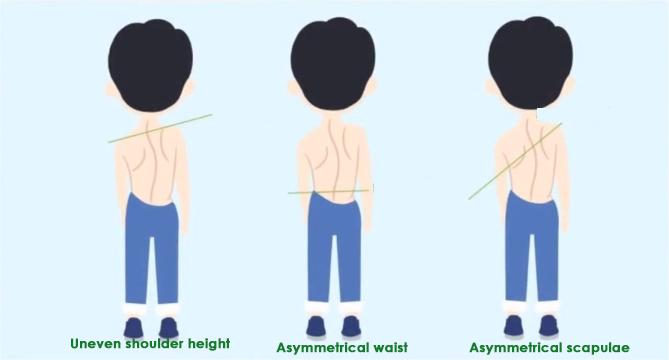
- Physical posture examination:
Visually observe the asymmetry of the child’s shoulders, shoulder blades, and hips. Pay attention to common abnormal symptoms of spinal scoliosis, such as unequal shoulder heights, waist asymmetry, and asymmetrical shoulder blades.
- Adams forward bending test: Observe the child’s back while they bend forward.
- Medical history inquiry and X-ray imaging examination.
4. How can spinal scoliosis be prevented?
- Engage in moderate exercise, including low- to moderate-intensity aerobic activities for 4-5 times a week, with each session lasting 1 hour.
- Maintain correct body posture.
- Ensure adequate rest and nutrition, and develop the habit of eating breakfast.
- Choose a suitable backpack and use a double-shoulder backpack.
- Pay attention to the child’s physical and mental health.
5. How is rehabilitation conducted?
Interventions for spinal scoliosis mainly include observation, exercise training, orthotic intervention, and physical therapy. Exercise training promotes local blood circulation, muscle balance adjustment, and spinal flexibility.
6. Exercise therapy for spinal scoliosis:
- Stand tall: Stand against a wall with both shoulders and buttocks touching the wall. Keep the chin slightly tucked, eyes looking straight ahead, arms naturally hanging down, and try to straighten the head, neck, and spine upwards. Maintain this position for 10 minutes.
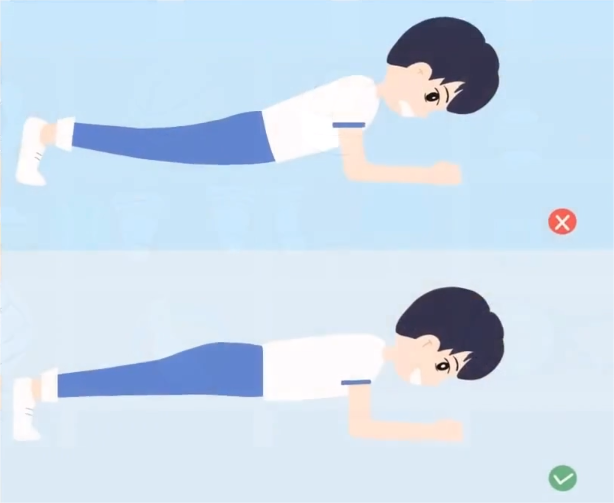
- Perform core stability training exercises, such as planks.
-Practice a unilateral flying motion, lifting the upper and lower limbs on the convex side for two minutes each time.
- Perform movements on a fitness ball towards the convex side for 30 seconds, repeating 5–6 times, with moderate fatigue.
If your child exhibits poor body postures such as hunching, uneven shoulders, or spinal deformities and you suspect spinal scoliosis, please seek medical attention from relevant professional institutions promptly.
In conclusion, the best approach to addressing spinal scoliosis in school-age children is to take preventive measures, undergo regular check-ups, and aim for early detection, diagnosis, and treatment.
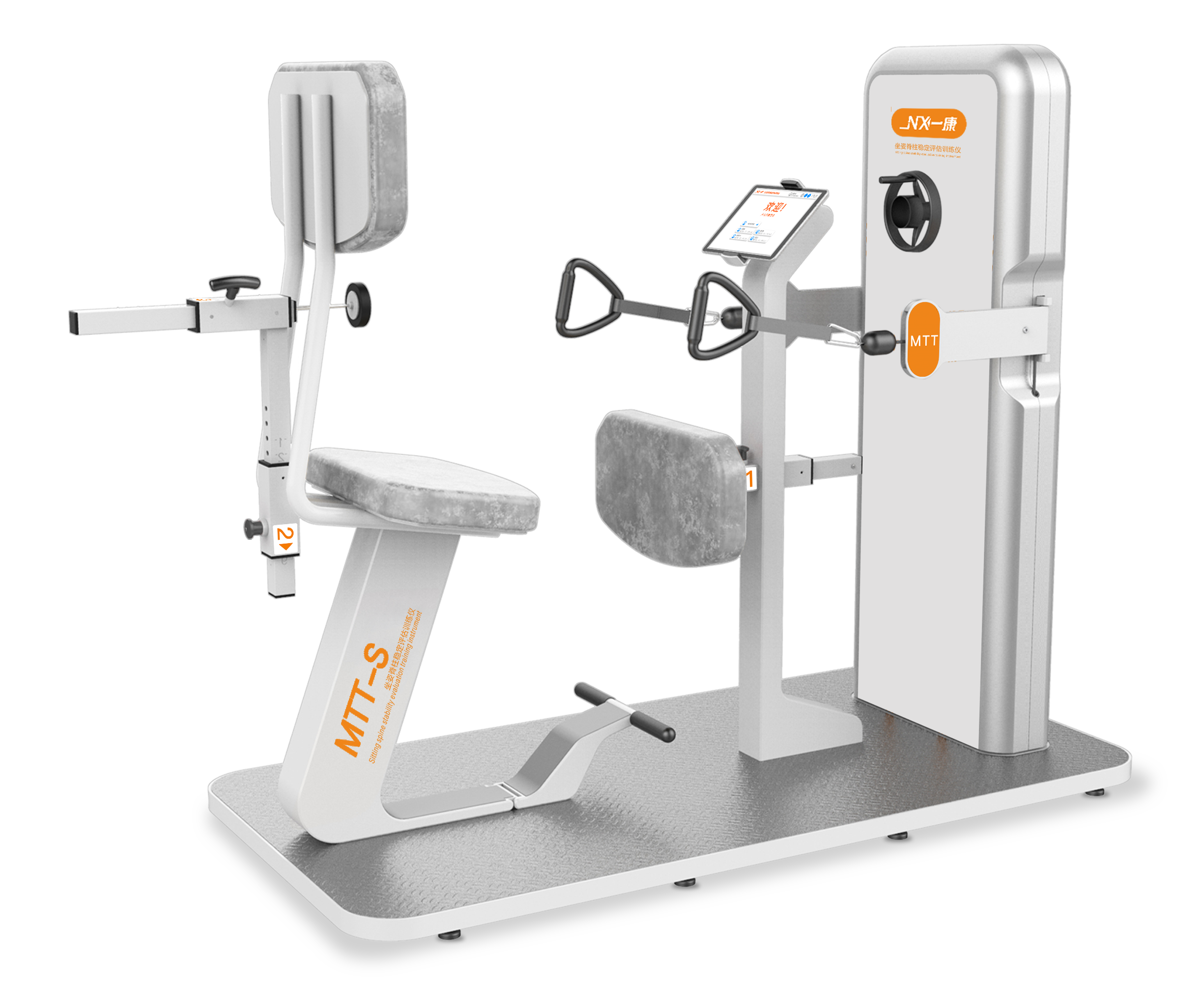
Sitting Spine Stability Assessment Training Instrument
The spinal stability assessment training instrument MTT-S is designed according to the biomechanics and ergonomics of human body movement so that patients can intuitively see the contraction control of their trunk stabilization muscles from the display screen during training. And according to the voice and visual prompts of the interactive game, conscious active control of the trunk, posture control, and effective activities are carried out so as to promote the “activation” and strengthening of the core muscles of the trunk, so as to achieve the purpose of rehabilitation.
More Article: Simple and practical home hand rehabilitation
Home exercises for frozen shoulder
Post time: Apr-12-2024