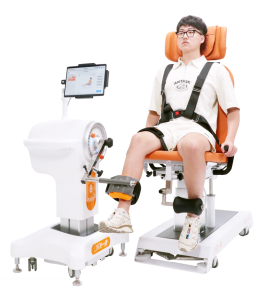
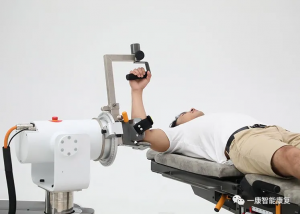
The human body is an intricate assembly of systems and structures, each with its distinct purpose and function. One such system that plays a critical role in physical mobility and flexibility is the skeletal system, specifically the joints. The degree to which a joint can move is referred to as its range of motion (ROM). This article explores the concept of joint range of motion, its importance, how it’s improved, and factors that can influence it.
1.What is Range of Motion?
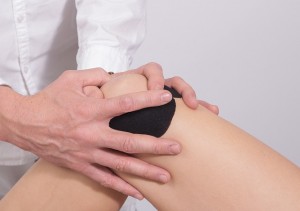
Range of Motion (ROM) refers to the normal extent of movement a joint can perform without causing discomfort or pain. It’s a fundamental measure of functionality in our joints, contributing to our ability to perform everyday tasks and engage in physical activities. ROM is typically measured in degrees and is integral to health-related fields such as orthopedics, physiotherapy, and sports medicine.
2.Types of Range of Motion
ROM can be divided into two types: active and passive.
Active ROM: This is the degree of movement a person can achieve by actively moving a joint using the muscles attached to it. For example, lifting your arm overhead is an active motion.
Passive ROM: This is the degree of movement at a joint when an external force is used. The external force could be a therapist moving the joint or using a device to facilitate movement.
3.Factors Affecting Range of Motion
Several factors can affect ROM, including:
1)Age: As people age, their joints tend to lose flexibility, which can reduce ROM.
2)Injury or Trauma: Injuries can cause swelling and pain, limiting the ROM.
3)Disease: Certain diseases like arthritis can lead to joint stiffness and reduce ROM.
4)Surgery: Post-surgery, ROM can be limited due to pain, swelling, or immobilization.
5)Inactivity: Lack of regular movement can lead to joint stiffness and reduced ROM.
4.The Importance of Maintaining ROM
Maintaining an optimal ROM is vital for overall health and well-being. It not only allows us to perform daily activities with ease but also helps in preventing injuries. A healthy ROM is also essential for athletes for optimal performance and injury prevention.
5.How to improve ROM?
1)Stretching exercises: Engaging in appropriate stretching exercises can increase joint flexibility and range of motion. Targeted stretching movements such as shoulder stretches, hip stretches, and knee stretches can specifically improve joint mobility.
2)Joint mobilization training: Joint mobilization training involves performing specific joint rolling, rotating, and swinging movements to increase joint range of motion and stability. This training can be done using equipment, assistive devices, or bodyweight exercises.
3)Strength training: Strength training can enhance the strength of the muscle groups that support the joints, thereby improving joint stability and mobility. Choose appropriate strength training exercises such as weightlifting, resistance training, or using resistance bands for exercise.
4)Aerobic exercise: Moderate aerobic exercise promotes joint blood circulation and nutrient supply, contributing to joint health and mobility. Opt for low-impact aerobic activities such as swimming, cycling, or jogging.
In conclusion, understanding and maintaining joint range of motion is crucial to overall mobility and physical health. Whether it’s through regular physical activity, physiotherapy, or medical intervention, ensuring a healthy ROM can significantly improve the quality of life and prevent potential physical complications.
Multi-Joint Isokinetic Strength Testing & Training System
Post time: Sep-15-2023