Being thin often means muscle attenuation and weakening of strength. When the limbs appear soft and slender, and the fat on the waist and abdomen accumulates, the body will become more and more prone to fatigue, and it is often difficult to walk or hold things. At this time, we must be vigilant- Sarcopenia.
So what is sarcopenia, why does it happen, and how to treat and prevent it?
1. What is sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia, also known as sarcopenia, is also called “skeletal muscle aging” or “sarcopenia” clinically, which refers to the decline in skeletal muscle mass and muscle strength caused by aging. The prevalence rate is 8.9% to 38.8%. It is more common in men than women, and the age of onset is more common in those over 60 years old, and the prevalence rate increases significantly with age.
The clinical manifestations often lack specificity, and the general symptoms are: weakness, slender limbs and weakness, easy falls, slow gait, and difficulty walking.
2. How is sarcopenia caused?
1) Primary factors
Aging causes a decrease in body hormone levels (testosterone, estrogen, growth hormone, IGF-1), a decrease in muscle protein synthesis, a decrease in the number of α motor neurons, attenuation of type II muscle fibers, abnormal mitochondrial function, oxidative damage, and apoptosis of skeletal muscle cells. Increased death, decreased number of satellite cells and decreased regenerative capacity, increased inflammatory cytokines, etc.
2) Secondary factors
①Malnutrition
Insufficient dietary intake of energy, protein and vitamins, improper weight loss, etc., prompt the body to use muscle protein reserves, the rate of muscle synthesis decreases, and the rate of decomposition increases, resulting in muscle atrophy.
②Disease status
Chronic inflammatory diseases, tumors, endocrine diseases or chronic heart, lung, kidney and other diseases will accelerate protein decomposition and consumption, muscle catabolism, and cause muscle loss.
③ Bad lifestyle
Lack of exercise: Long-term bed rest, braking, sedentary, too little activity can lead to insulin resistance and accelerate the rate of muscle loss.
Alcohol abuse: Long-term alcohol consumption can cause muscle type II fiber (fast-twitch) atrophy.
Smoking: Cigarettes reduce protein synthesis and accelerate protein degradation.
3. What are the harms of sarcopenia?
1) Decreased mobility
When muscle loss and strength decrease, people will feel weak, and have difficulty completing daily activities such as sitting, walking, lifting, and climbing, and gradually develop stumbling, difficulty getting out of bed, and inability to stand upright.
2) Increased risk of trauma
Sarcopenia often coexists with osteoporosis. Muscle attenuation can lead to poor movement and balance, and falls and fractures are extremely prone to occur.
3) Poor resistance and coping ability to stress events
A small adverse event can produce a domino effect. Elderly people with sarcopenia are prone to falls, and then fractures after the fall. After the fracture, hospitalization is required, and limb immobilization during and after hospitalization makes the elderly Further muscle atrophy and further loss of body functions will not only increase the care burden and medical expenses of the society and family, but also seriously affect the quality of life and even shorten the life span of the elderly.
4) Decreased immunity
10% muscle loss leads to decreased immune function and increased risk of infection; 20% muscle loss leads to weakness, decreased ability of daily living, delayed wound healing, and infection; 30% muscle loss leads to difficulty in sitting up independently, prone to pressure sores, and Disabling; 40% loss of muscle mass, significantly increased risk of death, such as death from pneumonia.
5) Endocrine and metabolic disorders
Muscle loss will lead to a decrease in the body’s insulin sensitivity, resulting in insulin resistance; at the same time, muscle loss will affect the body’s lipid balance, reduce the basal metabolic rate, and cause fat accumulation and metabolic disorders.
4. Treatment of sarcopenia
1) Nutritional support
The main purpose is to consume sufficient energy and protein, promote muscle protein synthesis, increase and maintain muscle mass.
2) Exercise intervention, exercise can significantly increase muscle mass and muscle strength.
①Resistance exercise (such as stretching elastic bands, lifting dumbbells or mineral water bottles, etc.) is the basis and core part of exercise intervention, which is characterized by a gradual increase in exercise intensity, and strengthens the whole body by increasing the cross-sectional area of type I and type II muscle fibers. Muscle mass, improved physical performance and pace.
②Aerobic exercise (such as jogging, brisk walking, swimming, etc.) can improve muscle strength and overall muscle coordination by improving mitochondrial metabolism and expression, improve cardiopulmonary function and activity capacity, improve endurance, reduce the risk of metabolic diseases, and reduce body weight. Fat ratio, improve immunity, enhance the body’s adaptability.
③Balance training can help patients maintain body stability in daily life or activities and reduce the risk of falls.

5. Prevention of sarcopenia
1) Pay attention to dietary nutrition
Routine nutritional screening for older adults. Avoid high-fat, high-sugar diets. Intake 1.2g/ (kg.d) of protein rich in leucine, supplement vitamin D appropriately, and eat more dark-colored vegetables, fruits and beans to ensure sufficient daily energy intake and prevent malnutrition.
2) Develop a healthy lifestyle
Pay attention to exercise, avoid absolute rest or sitting for a long time, exercise reasonably, step by step, and focus on not feeling tired; quit smoking and drinking, maintain a good attitude, spend more time with the elderly, and avoid depression.
3) Weight management
Maintain an appropriate body weight, avoid being overweight or underweight or fluctuate too much, and it is advisable to reduce it by no more than 5% within six months, so that the body mass index (BMI) can be maintained at 20-24kg/m2.
4) Pay attention to exceptions
If there are abnormal phenomena such as poor cardiopulmonary function, decreased activity, and easy fatigue, do not be careless, and go to the hospital for examination as soon as possible to avoid delaying the condition.
5) Strengthen inspection
It is recommended that people over the age of 60 do a physical examination or repeated falls, step up the pace test → grip strength assessment → muscle mass measurement, so as to achieve early detection and early treatment.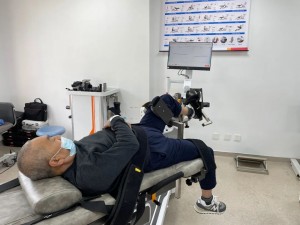
Post time: Jul-07-2023